Introduction to HTML

What is HTML?
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. "Markup language" means that, rather than using a programming language to perform functions, HTML uses tags to identify different types of content and the purposes they each serve to the webpage.- ★ HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- ★ HTML describes structure of a Web page .
- ★ HTML documents are described by HTML tags .
- ★ Each HTML tag describes different element.
HTML versions
| Version | Year |
|---|---|
| HTML | 1991 |
| HTML2.0 | 1995 |
| HTML3.2 | 1997 |
| HTML4.01 | 1999 |
| XHTML | 2000 |
| HTML5 | 2014 |
HTML Page Structure
There are always two parts to an HTML file: the head and the body.- ★ head : The head contains information about your HTML file, like its title. The title is what we see in the browser’s title bar or page tab.
- ★ body The body is where you put your content, such as text, images, and links. The content in the body is what will be visible on the actual page.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title></title> </head> <body> </body> </html>
- • The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document
- • The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page
- • The <head> element contains meta information about the HTML page
- • The <title> element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab)
- • The <body> element defines the document's body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
Pay attention to...
- • Always put <!DOCTYPE html> on the first line. This tells the browser what language it’s reading (in this case, HTML).
- • Always put <html> on the next line. This starts the HTML document.
- • Always put </html> on the last line. This ends the HTML document.
HTML Element
An HTML element is defined by a start tag , some content, and an end tag :<tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>
| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
| <h1> | My First Heading | </h1> |
| <p> | My first paragraph | </p> |
HTML Headings
- • HTML headings are defined with the <h1> </h1> to <h6> </h6> tags.
- • <h1> defines the most important heading.
- • <h6> defines the least important heading.

HTML Paragraphs
HTML paragraphs are defined with the <p> </p> tag:<p> This is a paragraph. </p>
Pay attention to...
- • Any number of spaces and newlines will be counted as only one space.
HTML Comment
HTML Comment are defined with the <!-- and --> tag:<!-- Comments here. -->
- •Comments are not displayed by the browser, but it will help you remember why you did certain things.
- •With comments you can place notifications and reminders in your HTML.
- •Comments tag: <!-- Comments Here --> (notce that there are at least two dashes on each side)
HTML attributes
- • HTML elements can have attributes .
- • Attributes provide additional information about an element.
- • Attributes are always specified in the start tag.
- • Attributes come in name/value pairs like : name = 'value'.
Example
1. The title attribute for <p></p>:<p title="our course name">CSCI 4410 Web Technologies</p>move your cursor above this paragraph:
CSCI 4410 Web Technologies
<a href="https://lecture.yangxinmtsu.repl.co/4410.html">CSCI 4410 Course Link</a>3. The src attribute for HTML image tag <img>:
<img src="image_name.jpg">
HTML Hyperlink
- •HTML link is a hyperlink.
- •Hyperlink is a text or image you can click on, and jump to another document.
<a href="https://lecture.yangxinmtsu.repl.co/4410" target="_blank">CSCI 4410 Course Link</a>
- • In HTML, links are defined with the <a> tag (a stands for anchor).
- • Hyperlink is a text or image you can click on, and jump to another document.
- • The href attribute specifies the destination address. The href attribute can be either absolute URL (a full web address) or local link.
- • The target attribute specifies where to open the linked document.
- • The link text is the visible part.
target attribute
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| _blank | Load in a new window |
| _self | Load in the same frame as it was clicked |
| _parent | Load in the parent frameset |
| _top | Load in the full body of the window |
Create a bookmark
- • HTML bookmarks are used to allow readers to jump to specific parts of a Web page.
- • Bookmarks are practical if your website has long pages.
- • To make a bookmark, you have to first create the bookmark (by the id attribute), then add a link (# and the value of the id attribute) to it.
- • Bookmark is just a link to some tag.
<h1 id="top">This is the top.</h1> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <a href="#top">Go to the top.</a>
HTML Images
- • HTML can display image formats like JPG, PNG, GIF, SVG, ....
- • The <img> tag is empty, it contains attributes only and does not have a closing tag.
- • HTML images are defined with the <img> tag:
<img src="mtsu.png" alt="MTSU Campus" width="200px" height="400px">
- • src : source image file, can be either local or online.
- • alt : specifies an alternate text for an image, if the image cannot be displayed.
- • width : image width, the values are specified in pixels.
- • height : image height, the values are specified in pixels.
more on src attribute
- • For an online image, we use its absolute/full url link.
<img src="https://mtsunews.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/MT-Tuition-Free-graphic-promo-web.jpg" width="200px" height="200px">
- Q: which one is better for your project?
HTML Lists
Unordered lists
- • An unordered list are defined with <ul> </ul> tag.
- • Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
<ul> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Milk</li> </ul>

| list-style-type | Description |
|---|---|
| disc | Sets the list item marker to a bullet (default) |
| circle | Sets the list item marker to a circle |
| square | Sets the list item marker to a square |
| none | The list items will not be marked |

Ordered list
- • An Ordered list starts with the <ol> </ol>
- • Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
<ol> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Milk</li> </ol>

| type | Description |
|---|---|
| type="1" | The list items will be numbered with numbers (default) |
| type="A" | The list items will be numbered with uppercase letters |
| type="a" | The list items will be numbered with lowercase letters |
| type="I" | The list items will be numbered with uppercase roman numbers |
| type="i" | The list items will be numbered with lowercase roman numbers |

Nested lists
<ol type="1"> <li>Coffee</li> <ul> <li>Espresso</li> <li>Cappuccino</li> </ul> <li>Tea</li> <li>Milk</li> </ol>

HTML Table
- • HTML tables allow web developers to arrange data into rows and columns .
- • Tables are defined with the <table> </table> tag.
- • <th> Defines a header cell in a table
- • Tables are divided into table rows with the <tr> tag.
- • Table rows are divided into table data with the <td> tag.
- • If you do not specify a border for the table, it will be displayed without borders:
<table>
<!-- first row: headers -->
<tr>
<th>Course Title</th>
<th>Course Name</th>
</tr>
<!-- second row -->
<tr>
<td>CSCI 3080</td>
<td>Discrete Structure</td>
</tr>
<!-- third row -->
<tr>
<td>CSCI 4410</td>
<td>Web Technologies</td>
</tr>
</table>

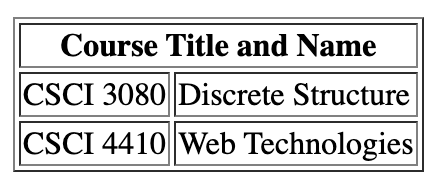
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<th>Course Title</th>
<th>Course Name</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>CSCI 3080</td>
<td>Discrete Structure</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>CSCI 4410</td>
<td>Web Technologies</td>
</tr>
</table>
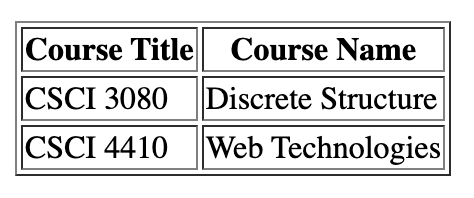
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<th colspan="2">Course Title and Name</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>CSCI 3080</td>
<td>Discrete Structure</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>CSCI 4410</td>
<td>Web Technologies</td>
</tr>
</table>
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<th>Course Title</th>
<th>Course Name</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="2">CSCI 3080</td>
<td>Discrete Structure</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Web Technologies</td>
</tr>
</table>

Modern Table Structure: <thead> and <tbody>
- • In modern HTML, we can split a table into a header part and a body part.
- • <thead> groups header rows.
- • <tbody> groups data rows.
- • This improves readability and helps screen readers understand tables.
<table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>Version</th> <th>Year</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td>HTML</td> <td>1991</td> </tr> <tr> <td>HTML5</td> <td>2014</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
HTML Formatting
HTML Bold vs Strong
- • The HTML <b> element defines bold text, without any extra importance.
- • The HTML <strong> element defines text with strong importance.
- • By default, <b> and <strong> may look the same, but their meanings are different.
HTML Italic vs Emphasis
- • The HTML <i> element defines italic text, without any extra importance.
- • The HTML <em> element defines text with emphasis.
- • By default, <i> and <em> may look the same, but their meanings are different.
HTML Marked
- • The HTML <mark> element defines marked or highlighted text.
Examples
<p>This text is normal.</p> <p><b>This text is bold (style only).</b></p> <p><strong>This text is strong (important).</strong></p> <p><i>This text is italic (style only).</i></p> <p><em>This text is emphasized (meaning).</em></p> <p><mark>This text is marked.</mark></p>
This text is normal.
This text is bold (style only).
This text is strong (important).
This text is italic (style only).
This text is emphasized (meaning).
This text is marked.
Quick Guideline
- • Use <strong> and <em> when the text is important or emphasized.
- • Use <b> and <i> only for visual styling or labels.
Basic HTML Page Structure
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>My Webpage</title> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Understanding Meta Tags in HTML
<meta charset="UTF-8">
What it does
This line tells the browser how to display the text characters correctly in your HTML file.
Why it matters
- UTF-8 supports almost all characters in the world:
- English letters
- Accented characters (é, ñ)
- Symbols (©, ★)
- Emojis 😊
- Without this line, some characters may display incorrectly.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
What it does
This line controls how the webpage is displayed on different screen sizes, especially phones and tablets. This line helps your webpage look correct on phones and tablets.
-
width=device-width
-> Make the page width match the device screen width. -
initial-scale=1.0
--> Show the page at normal size (no zoom in or out).
Why it matters
- Without this line, webpages often look tiny or zoomed out on mobile devices.
- With it, pages are mobile-friendly by default.
HTML Editors
- • Notepad++
- • Atom
- • vi/vim/emac
- • sublime
- • Online Editor: replit
HTML tip: use lowercase tags
- • HTML tags are not case sensitive, <P> means the same as <p>.
- • If you want to view the HTML source, right-click in the page and select "View Page Source" (in Chrome) or "View Source" (in IE), or similar in another browser. This will open a window containing the HTML code of the page.
Indentation is your friend
Indentation really helps make your code more readable!Process for developing a website
- ☆ Plan and design the website
- ☆ Create the web pages using an editor
- ☆ Test the web pages
- ☆ Publish the web pages by uploading the pages to the web server.