Recursive Functions in C++
Recursive Functions
- ★ A recursive function is a function that calls itself.
- ★ Recursive problem solving
- ☆ Base case
- ☆ Divide the rest of problem into subproblem and do recursive call
- ★ There are many problems that lend themselves to recursive solutions:
- ☆ Mathematic -- factorial, Fibonacci, ......
- ☆ Searching and sorting -- binary search, serach trees, ......
Example -- Factorial
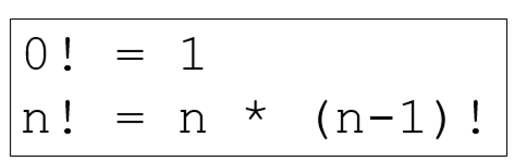
- ★ Base case:
- ☆ factorial(0) = 1
- ★ Recursive case:
- ☆ factorial(n) = n*factorial(n-1)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//function prototype
int factorial(int n);
int main()
{
//function activation
cout << factorial(8) << endl;
return 0;
}
//function definition
int factorial(int n)
{
if(n == 0) //base case
return 1;
return n*factorial(n-1); //recursive case
}
factorial.cpp
Example - Fibonacci

- ★ Base case:
- ☆ Fib(0) = 0
- ☆ Fib(1) = 1
- ★ Recursive case:
- ☆ Fib(n) = Fib(n-1) + Fib(n-2)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//function prototype
int fibonacci(int n);
int main()
{
//function activation
cout << fibonacci(5) << endl;
cout << fibonacci(12) << endl;
cout << fibonacci(30) << endl;
return 0;
}
//function definition
int fibonacci(int n)
{
if(n <= 1) //base case
return n;
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2); //recursive case
}
fibonacci.cpp
Important notes:
- ★ If recursion doesn't eventually stop you will have infinite recursion
- ★ Recursion can be resource intensive
- ★ Remember the base case(s)
- ☆ It terminates the recursion
- ★ Only use recursive solutions when it makes sense.
- ★ Anything that can be done recursively can be done iteratively.
Recursion vs Iteration
- ★ Infinite recursion occurs if the recursion step does not reduce the problem in a manner that converges on some condition (base case) and Infinite recursion can crash the system.
- ★ Recursion is usually slower than iteration due to the overhead of maintaining the stack.
- ★ Recursion uses more memory than iteration.
- ★ Recursion makes the code smaller.
- ★ An iteration does not use the stack so it's faster than recursion.
- ★ Iteration consues less memory.
- ★ Iteration makes the code longer.